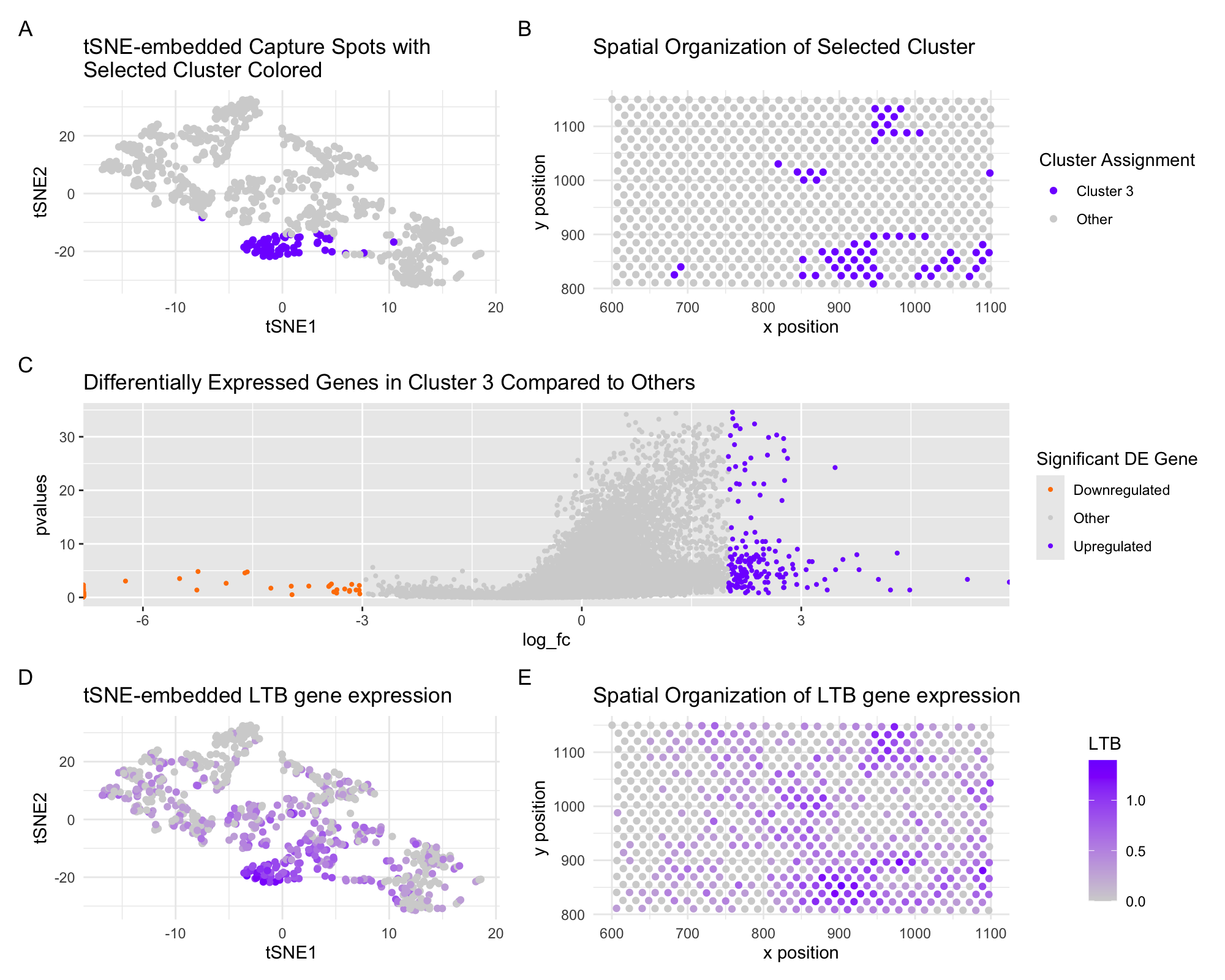
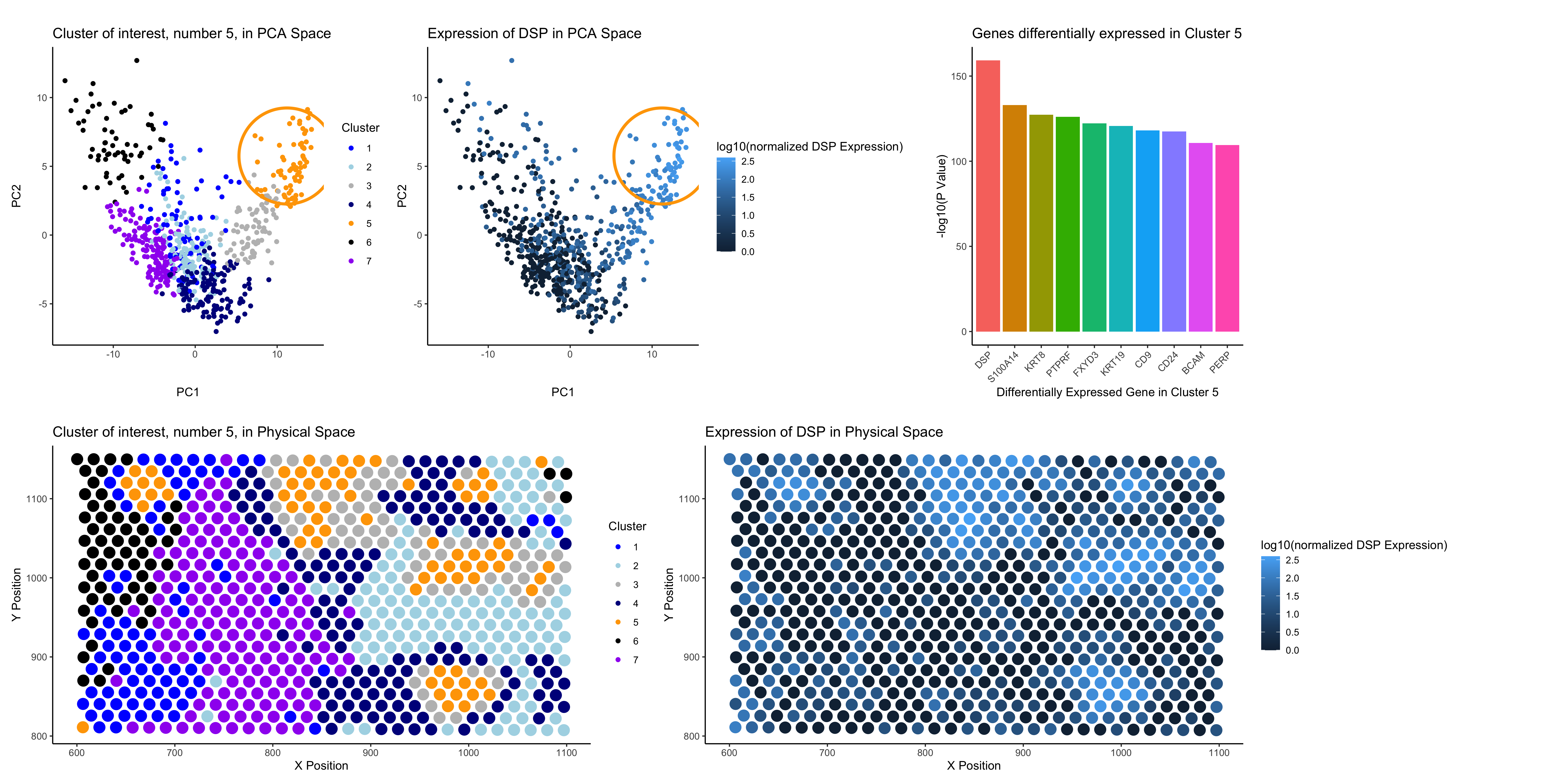
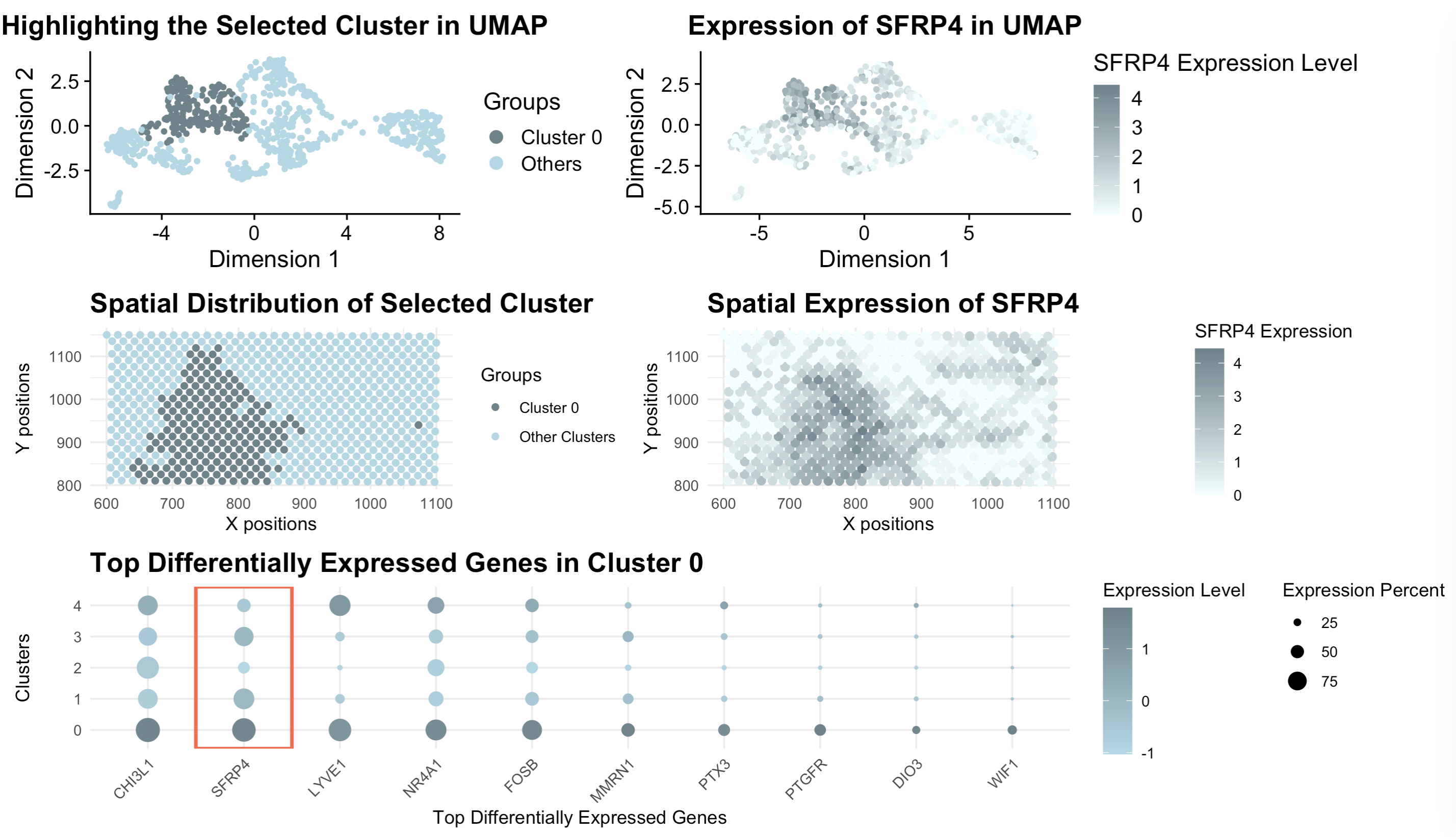
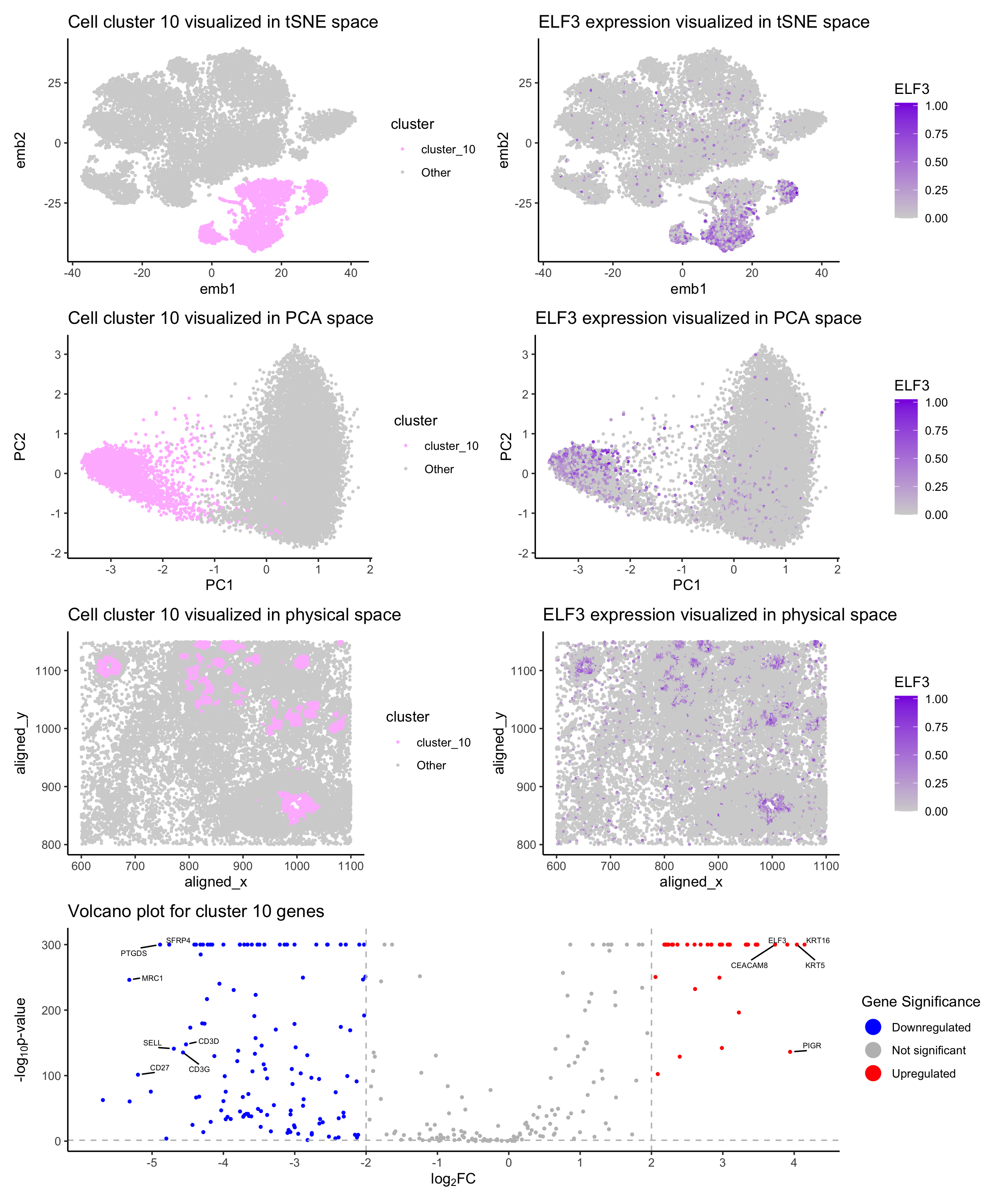
Welcome
Welcome to the Course Website for EN.580.428 Genomic Data Visualization!
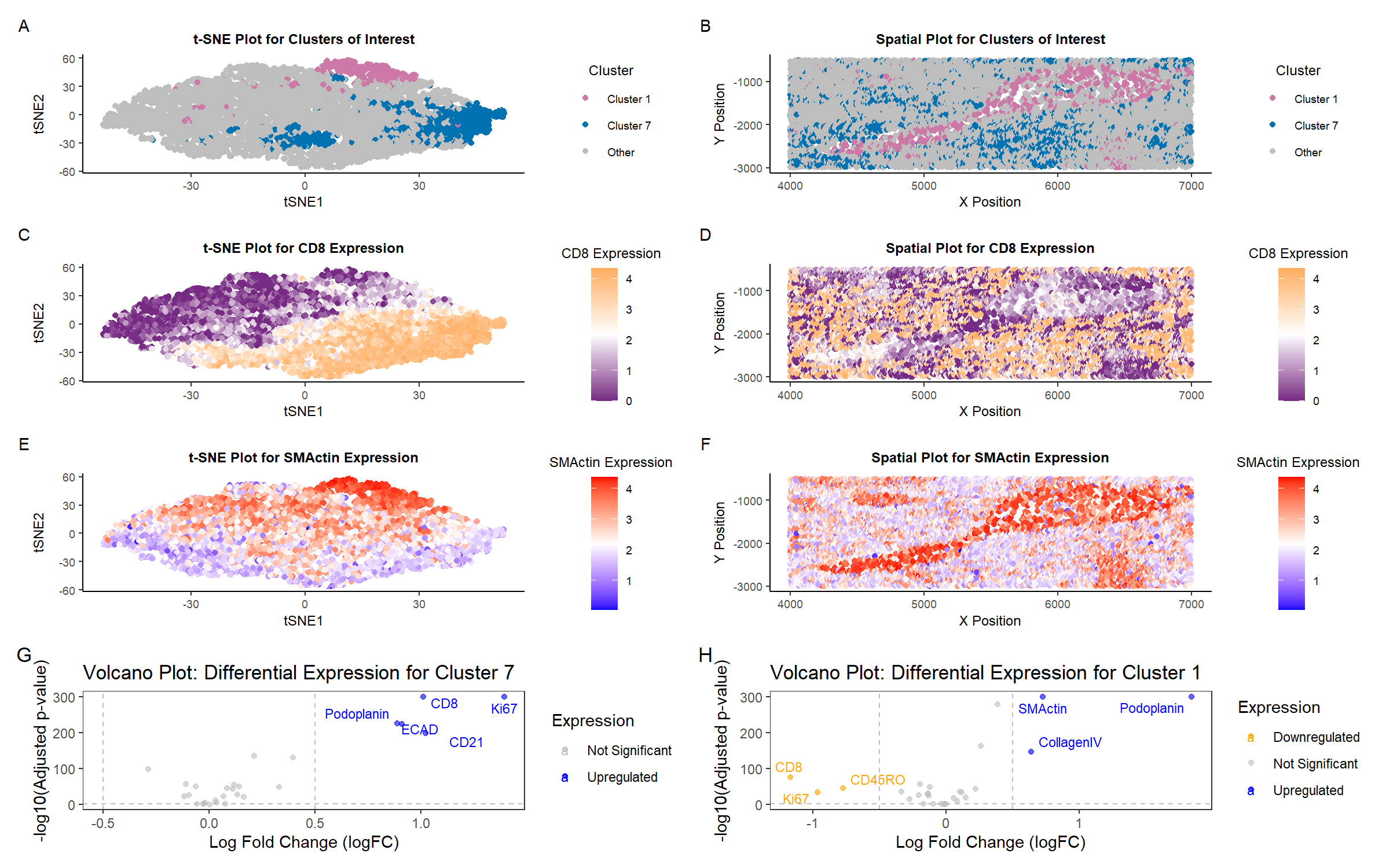
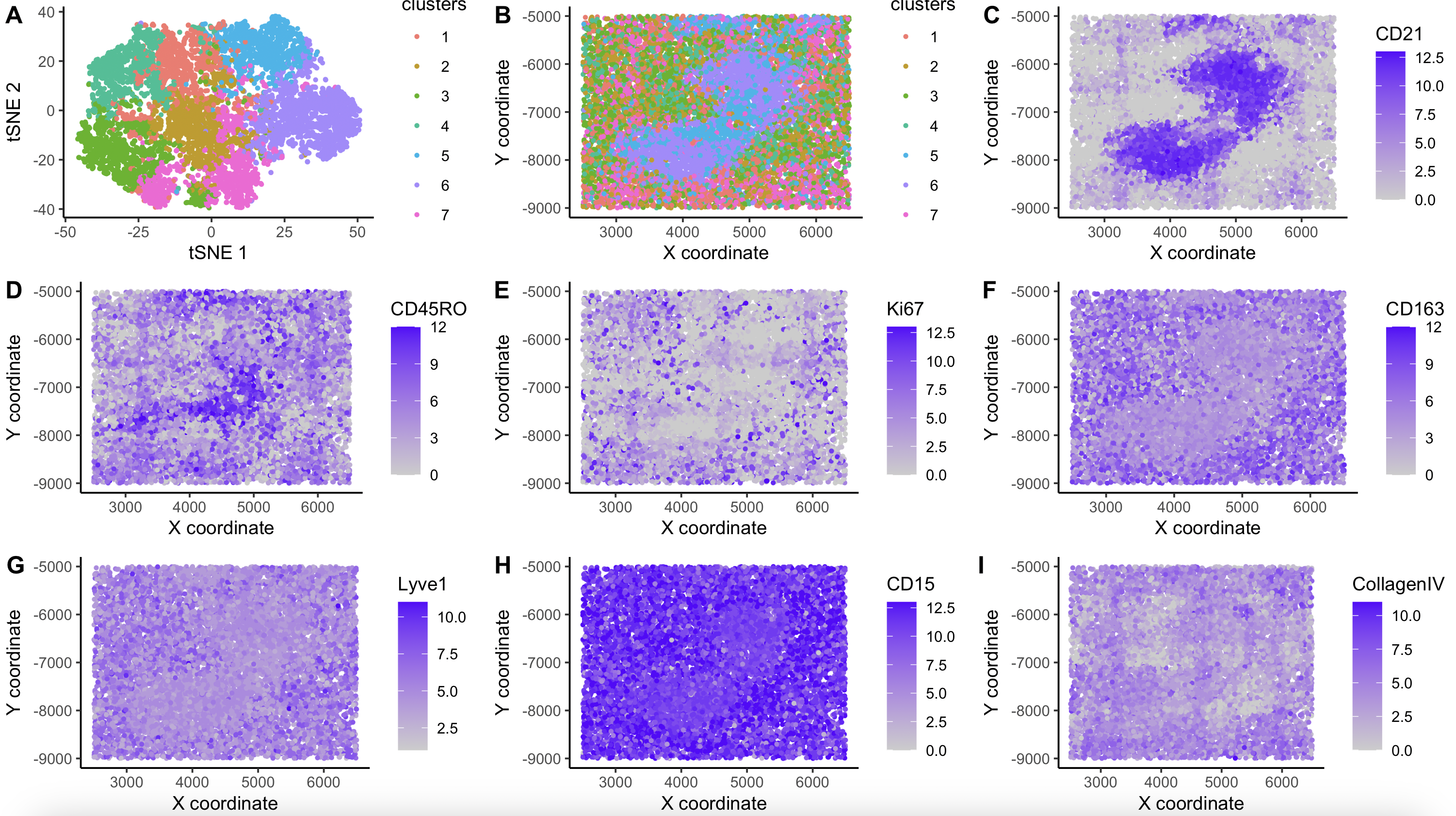
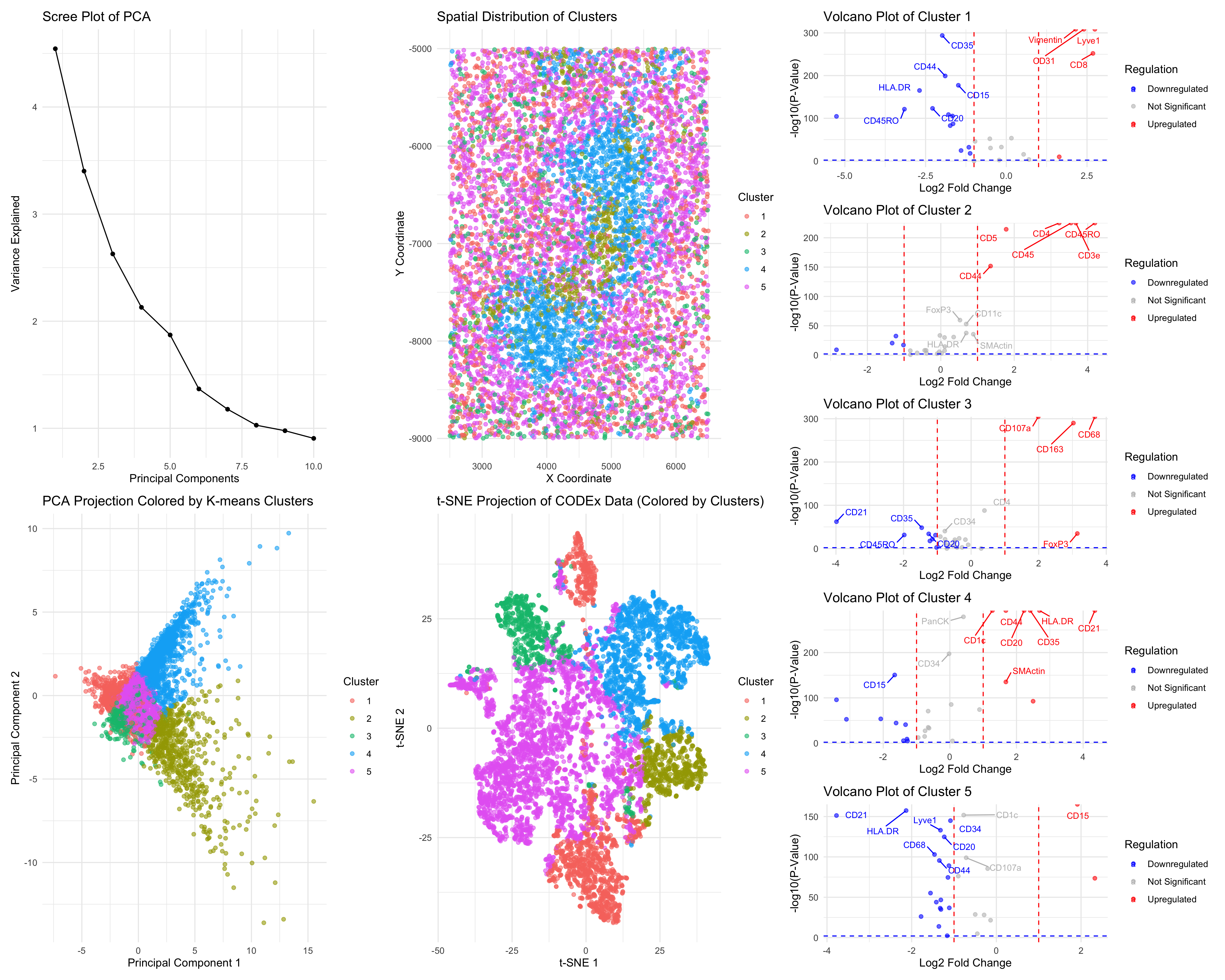
As the primary mode through which analysts and audience members alike consume data, data visualization remains an important hypothesis generating and analytical technique in data-driven research to facilitate new discoveries. However, if done poorly, data visualization can also mislead, bias, and slow down progress. This hands-on course will cover the principles of perception and cognition relevant for data visualization and apply these principles to genomic data, including large-scale single-cell and spatially-resolved omics datasets, using the R statistical programming language. Students will be expected to complete class readings, create weekly data visualizations as homework assignments, and make a major class presentation.
Course Information
Course Staff: Prof. Jean Fan and Caleb Hallinan
Lectures: 8:00am-9:50am Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. See Canvas for location details.
Office Hours: 10:00am-10:50am Monday, Wednesday, and by request. See Canvas for location details.