Multimodal analysis of cell-type using gene expression patterns
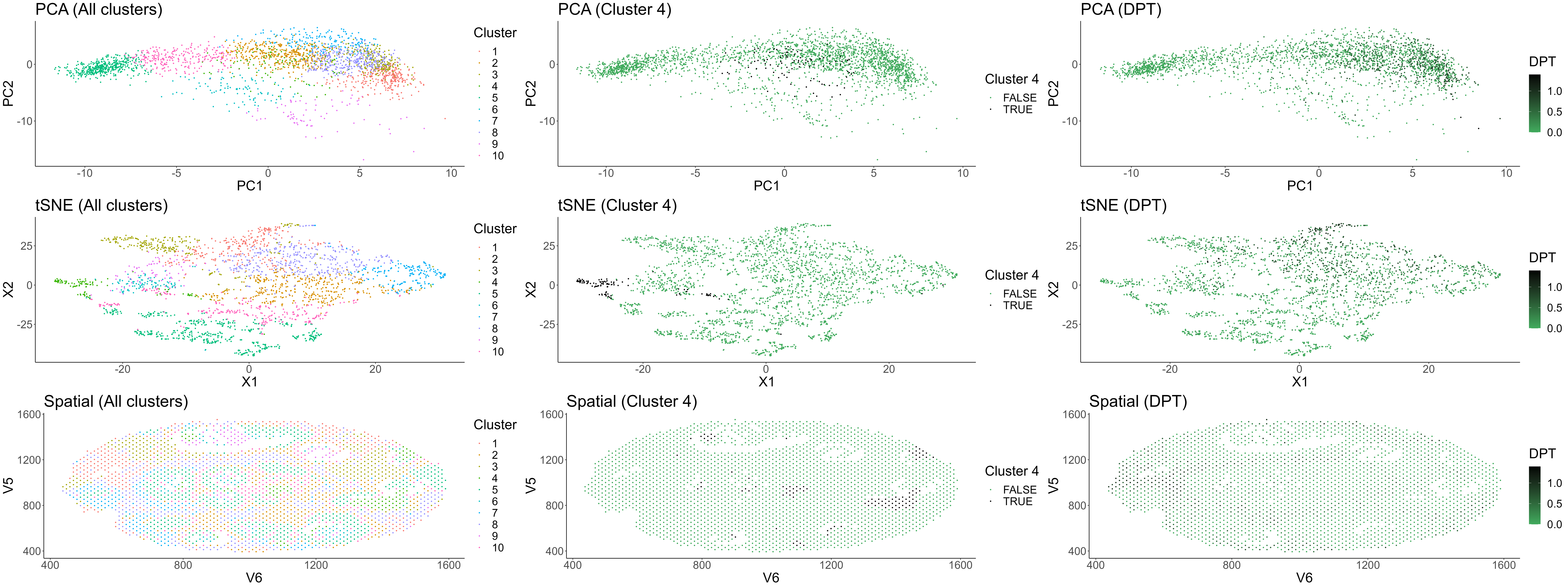
The raw gene expression data set was normalized by dividing each gene of each cell by the total number of genes for that cell. This amount is then multiplied by the median of the total number of genes in all cells. In other words, the raw gene expression data set was normalized such that each cell’s gene expression corresponds to the number of genes that would be expressed if each cell expressed the median value of the overall gene count. Next, this normalized data set was log10 converted to get a distribution that was more Gaussian. Following normalization and modification, k-means clustering was used to evaluate the data set. The (WSS) and (BSS) were plotted against the number of clusters ranging from 1 to 50. The number of clusters chosen for subsequent analysis was 10, as it was observed to be the point at which the change in WSS and BSS plateaued. The dataset underwent principal component analysis (PCA) and t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (tSNE) for visualization. Additionally, differentially expressed genes were identified for each cluster, by comparing the expression levels of genes in each cluster with those in the remaining clusters. A volcano plot was generated for the 10 identified clusters, with clusters 4 and 7 highlighting downregulated genes in blue and upregulated genes in red that surpassed the significance threshold, as indicated by the black dashed line. These genes also displayed a large fold change, as demonstrated by their position outside the black dashed lines for the log2 fold change threshold. The identified upregulated genes were SLC11A1, AQP9, CD36, ILRN, PLA2G7, FABP4, and MMP9, while the downregulated genes were PODN, IGF1, ELN, FZD4, and DPT. Cluster 4 was selected as the cluster of interest. To identify the most significant gene, a new data frame with the most significant genes was created by filtering the differential expression data by “Up” and “Down” categories. This data frame was sorted by p-values in decreasing order, and the most significant gene was selected as the gene with the highest p-value. In this analysis, the most significant gene was found to be DPT, which was a downregulated gene. Given the significance of DPT, it was selected as the gene of interest for creating multi-panel graphs of PCA, tSNE, and Spatial visualization for all clusters, cluster 4, and DPT. The graphs were designed to highlight the differences and similarities between each of the visualizations, with colors ranging from lighter to darker shades of green. Based on the GeneCards website, the DPT gene has a role in the fibroblast cell type. This code references the visualization source code written by the student Gohta.: https://jef.works/genomic-data-visualization-2023/blog/2023/02/17/gaihara1/ Other references: https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=DPT
##Code:
load library
library(ggplot2) library(Rtsne) library(gridExtra) library(ggrepel)
set seed for reproducibility
set.seed(0)
set 1x1 plot space
par(mfrow=c(1,1))
read in data
data <- read.csv(‘~/Downloads/visium_breast_cancer.csv.gz’ , row.names = 1) gexp <- data[,3:ncol(data)] genes <- colnames(gexp) pos <- data[,1:2]
data exploration
normalize
totgexp <- rowSums(gexp) mat <- gexp/rowSums(gexp) * median(rowSums(gexp)) mat <- log10(mat + 1)
kmeans clustering
characterize kmeans clustering
find optimal number of k
ks <- 1:50
loop through ks to return wss and bss as matrix
out <- do.call(rbind, lapply(ks, function(k) { com <- kmeans(mat, centers = k) c(within = com$tot.withinss, between = com$betweenss) })) plot(ks,out[,1],type=’b’,main=’WSS’) plot(ks,out[,2],type=’b’,main=’BSS’)
kmeans clustering
num_center = 10 com <- kmeans(mat, centers=num_center)
PCA analysis
pcs <- prcomp(mat)
tSNE analysis
emb <- Rtsne(mat)
plot tSNE analysis results
df <- data.frame(pos, emb$Y, celltype = as.factor(com$cluster)) head(df) p1 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = V6, y = V5, col=celltype)) + geom_point(size = 0.3) + scale_color_manual(values=c(“#1b9e77”, “#d95f02”, “#7570b3”, “#e7298a”, “#66a61e”, “#e6ab02”, “#a6761d”, “#666666”, “#1f78b4”, “#b2df8a”, “#33a02c”, “#fb9a99”, “#e31a1c”, “#fdbf6f”, “#ff7f00”)) + theme_classic() p2 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = X1, y = X2, col=celltype)) + geom_point(size = 0.3) + scale_color_manual(values=c(“#1b9e77”, “#d95f02”, “#7570b3”, “#e7298a”, “#66a61e”, “#e6ab02”, “#a6761d”, “#666666”, “#1f78b4”, “#b2df8a”, “#33a02c”, “#fb9a99”, “#e31a1c”, “#fdbf6f”, “#ff7f00”)) + theme_classic() grid.arrange(p1,p2)
loop through each cluster to find differentially expressed genes for each cluster vs. remaining clusters
volcano_plt <- lapply(seq_len(num_center), function(i) { ## pick a cluster cluster.of.interest <- names(which(com$cluster == i)) cluster.other <- names(which(com$cluster != i))
## loop through my genes and test each one out <- sapply(genes, function(g) { a <- mat[cluster.of.interest, g] b <- mat[cluster.other, g] pvs <- wilcox.test(a,b,alternative=’two.sided’)$p.val #pvs <- as.data.frame(pvs) log2fc <- log2(mean(a)/mean(b)) #log2fc <- as.data.frame(log2fc) c(pvs=pvs,log2fc=log2fc) })
## volcano plot # run Bonferroni correction determine a p value cutoff (conservative method with low false-positive rate but high false-negative rate as a trade-off) cutoff.pvs <- 0.05/ncol(mat) # false-positive rate would be 1-(1-0.05/ncol(mat))^ncol(mat) cutoff.log2fc <- 2 df <- data.frame(pvs=out[1,], log2fc=out[2,]) ## prepare a data frame for plotting df2 <- df # add a column of NAs to df2 titled diffexpressed df2$diffexpressed <- ‘NO’ # if log2fc > cutoff.log2fc and pvalue < cutoff.pvs, set as “Up” df2$diffexpressed[df2$log2fc > cutoff.log2fc & df2$pvs < cutoff.pvs] <- “Up” # if log2fc < -cutoff.log2fc and pvalue < cutoff.pvs, set as “Down” df2$diffexpressed[df2$log2fc < -cutoff.log2fc & df2$pvs < cutoff.pvs] <- “Down” # add a column of NAs to df2 titled genelabel that will contain names of differentially expressed genes df2$genelabel <- NA df2$genelabel[df2$diffexpressed != ‘NO’] <- rownames(df2)[df2$diffexpressed != ‘NO’]
plt <- ggplot(df2, aes(x=log2fc,y=-log10(pvs), col=diffexpressed, label=genelabel)) + geom_point() + scale_color_manual(values = c(‘blue’, ‘black’, ‘red’), name = ‘Expression’, breaks = c(‘Down’, ‘NO’, ‘Up’), labels = c(‘Down’, ‘N.S.’, ‘Up’)) + ggtitle(paste(‘Cluster’,i,’vs. Other Clusters’)) + xlab(‘log2 fold change’) + ylab(‘-log10(p value)’) + #geom_label_repel() + geom_vline(xintercept = c(-cutoff.log2fc, cutoff.log2fc), col=’black’,linetype=’dashed’) + geom_hline(yintercept = -log10(cutoff.pvs), col=’black’,linetype=’dashed’) + theme_classic()
plt })
save all figures
for (i in seq_len(num_center)) { name = paste0(‘volcano_cluster_‘,i,’_vs_otherclusters.png’) plt <- volcano_plt[[i]] ggsave(name, plot = plt, width = 10, height = 10, dpi = 300) }
#cluster 4 and 7 are the most significant according to volcano plot cluster4 <- df[df$celltype == 4, ] cluster7 <- df[df$celltype == 7, ] head(cluster4) head(cluster7)
compare two clusters against each other
num_cluster1 = 4 num_cluster2 = 7 cluster.of.interest <- names(which(com$cluster == num_cluster1)) cluster.other <- names(which(com$cluster != num_cluster2))
loop through my genes and test each one
out <- sapply(genes, function(g) { a <- mat[cluster.of.interest, g] b <- mat[cluster.other, g] pvs <- wilcox.test(a,b,alternative=’two.sided’)$p.val log2fc <- log2(mean(a)/mean(b)) c(pvs=pvs,log2fc=log2fc) })
volcano plot
run Bonferroni correction determine a p value cutoff (conservative method with low false-positive rate but high false-negative rate as a trade-off)
cutoff.pvs <- 0.05/ncol(mat) # false-positive rate would be 1-(1-0.05/ncol(mat))^ncol(mat) cutoff.log2fc <- 2 df <- data.frame(pvs=out[1,], log2fc=out[2,])
prepare a data frame for plotting
df2 <- df
add a column of NAs to df2 titled diffexpressed
df2$diffexpressed <- ‘NO’
if log2fc > cutoff.log2fc and pvalue < cutoff.pvs, set as “Up”
df2$diffexpressed[df2$log2fc > cutoff.log2fc & df2$pvs < cutoff.pvs] <- “Up”
if log2fc < -cutoff.log2fc and pvalue < cutoff.pvs, set as “Down”
df2$diffexpressed[df2$log2fc < -cutoff.log2fc & df2$pvs < cutoff.pvs] <- “Down”
add a column of NAs to df2 titled genelabel that will contain names of differentially expressed genes
df2$genelabel <- NA df2$genelabel[df2$diffexpressed != ‘NO’] <- rownames(df2)[df2$diffexpressed != ‘NO’]
#get a df with the most significant genes df2_up <- df2[df2$diffexpressed == “Up”, ] df2_down <- df2[df2$diffexpressed == “Down”, ]
significant_genes_df <- rbind(df2_up, df2_down) head(significant_genes_df)
significant_genes_df <- significant_genes_df[order(significant_genes_df$pvs, decreasing = TRUE), ] most_significant_gene <- significant_genes_df[1, “genelabel”]
most_significant_gene
plt <- ggplot(df2, aes(x=log2fc,y=-log10(pvs), col=diffexpressed, label=genelabel)) + geom_point() + scale_color_manual(values = c(‘blue’, ‘black’, ‘red’), name = ‘Expression’, breaks = c(‘Down’, ‘NO’, ‘Up’), labels = c(‘Down’, ‘N.S.’, ‘Up’)) + ggtitle(paste(‘Cluster’,num_cluster1,’vs. Cluster’,num_cluster2)) + xlab(‘log2 fold change’) + ylab(‘-log10(p value)’) + #geom_label_repel() + geom_vline(xintercept = c(-cutoff.log2fc, cutoff.log2fc), col=’black’,linetype=’dashed’) + geom_hline(yintercept = -log10(cutoff.pvs), col=’black’,linetype=’dashed’) + theme_classic()
name = paste0(‘volcano_cluster_‘,num_cluster1,’vs_cluster‘,num_cluster2,’.png’) ggsave(name, plt, width = 10, height = 10, dpi = 300)
plot for a figure
set custom theme for plots
plot_theme <- theme_classic() + theme( text = element_text(size = 25), legend.key.size = unit(0.75, ‘cm’) )
set the green color palette
green_palette <- c(“#e5f5e0”, “#c7e9c0”, “#a1d99b”, “#74c476”, “#41ab5d”, “#238b45”, “#006d2c”, “#00441b”)
plot certain cluster on tSNE and spatial
cluster.of.interest = 4 gene.of.interest = ‘DPT’ #most significant gene chosen from the list /down regulated df <- data.frame(pos, pcs$x[,1:2], emb$Y, celltype = as.factor(com$cluster), gene=mat[,gene.of.interest]) head(df)
PCA plots
p1 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = PC1, y = PC2, col = celltype)) + geom_point(size = 0.5) + ggtitle(‘PCA (All clusters)’) + labs(color = ‘Cluster’) + plot_theme p2 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = PC1, y = PC2, col = celltype == cluster.of.interest)) + geom_point(size = 0.5) + scale_color_manual(values = c(green_palette[5], ‘black’), name = paste(‘Cluster’,cluster.of.interest), labels = c(‘FALSE’,’TRUE’)) + ggtitle(paste0(‘PCA (Cluster ‘,cluster.of.interest,’)’)) + plot_theme p3 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = PC1, y = PC2, col = gene)) + geom_point(size = 0.5) + scale_color_gradient(low=green_palette[5], high=’black’, name = gene.of.interest) + ggtitle(paste0(‘PCA (‘,gene.of.interest,’)’)) + plot_theme
tSNE plots
p4 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = X1, y = X2, col = celltype)) + geom_point(size = 0.5) + ggtitle(‘tSNE (All clusters)’) + labs(color = ‘Cluster’) + plot_theme p5 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = X1, y = X2, col = celltype == cluster.of.interest)) + geom_point(size = 0.5) + scale_color_manual(values = c(green_palette[5], ‘black’), name = paste(‘Cluster’,cluster.of.interest), labels = c(‘FALSE’,’TRUE’)) + ggtitle(paste0(‘tSNE (Cluster ‘,cluster.of.interest,’)’)) + plot_theme p6 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = X1, y = X2, col = gene)) + geom_point(size = 0.5) + scale_color_gradient(low=green_palette[5], high=’black’, name = gene.of.interest) + ggtitle(paste0(‘tSNE (‘,gene.of.interest,’)’)) + plot_theme
spatial plots
p7 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = V6, y = V5, col = celltype)) + geom_point(size = 0.5) + ggtitle(‘Spatial (All clusters)’) + labs(color = ‘Cluster’) + plot_theme
spatial plots
p8 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = V6, y = V5, col = celltype == cluster.of.interest)) + geom_point(size = 0.5) + scale_color_manual(values = c(green_palette[5], ‘black’), name = paste(‘Cluster’, cluster.of.interest), labels = c(‘FALSE’, ‘TRUE’)) + ggtitle(paste0(‘Spatial (Cluster ‘, cluster.of.interest, ‘)’)) + plot_theme
p9 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = V6, y = V5, col = gene)) + geom_point(size = 0.5) + scale_color_gradient(low = green_palette[5], high = ‘black’, name = gene.of.interest) + ggtitle(paste0(‘Spatial (‘, gene.of.interest, ‘)’)) + plot_theme
volcano plot
p10 <- volcano_plt[[cluster.of.interest]] + geom_label_repel(size = 7) + plot_theme
lay <- rbind(c(1,2,3), c(4,5,6), c(7,8,9))
plot_theme <- plot_theme + theme(plot.width = unit(5, “cm”), plot.height = unit(5, “cm”))
result <- grid.arrange(p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9, layout_matrix = lay)
save panel plots
ggsave(“hw6_moneera_panels.png”, plot = result, width = 40, height = 15, dpi = 300)
save volcano plot
ggsave(“hw6_moneera_volcano.png”, plot = p10, width = 10, height = 10, dpi = 300)
